Steps involved in Guided implant surgery?
Guided implant surgery involves several steps:
- 3D Imaging: The dentist will first take a 3D image of the patient’s jaw using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) or a similar technology. This creates a detailed 3D model of the patient’s jawbone, allowing the dentist to plan the implant placement with great accuracy.
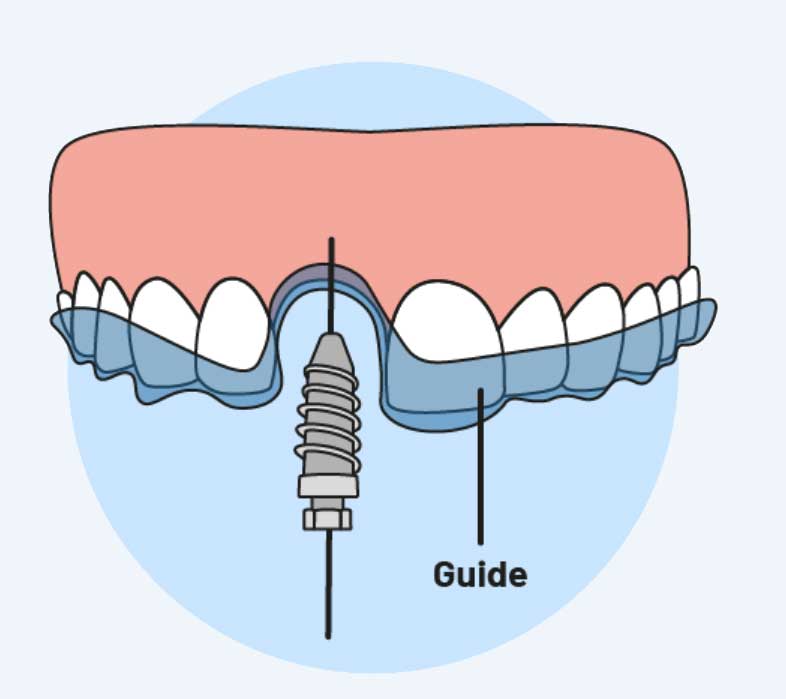
- Virtual Planning: The dentist will use specialized software to create a virtual model of the patient’s jawbone, which they will use to plan the implant placement. They will also design a surgical guide that fits over the patient’s teeth and serves as a template for the implant placement.
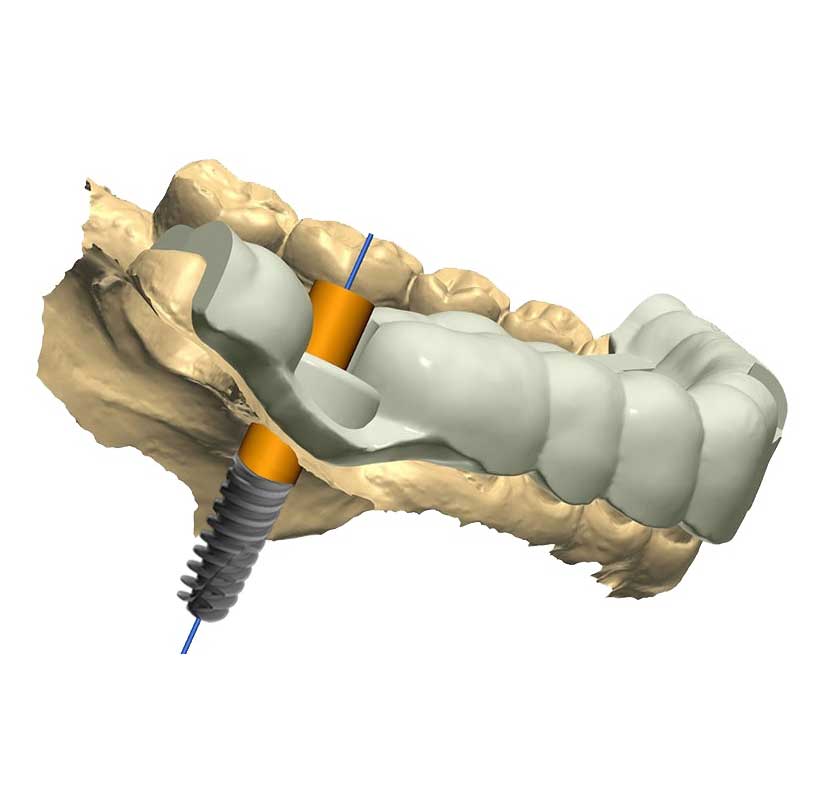
- Surgical Guide Fabrication: The surgical guide is 3D printed or otherwise manufactured, ensuring that it is an exact replica of the virtual model. The dentist will verify that the surgical guide fits correctly and accurately reflects the planned implant placement.
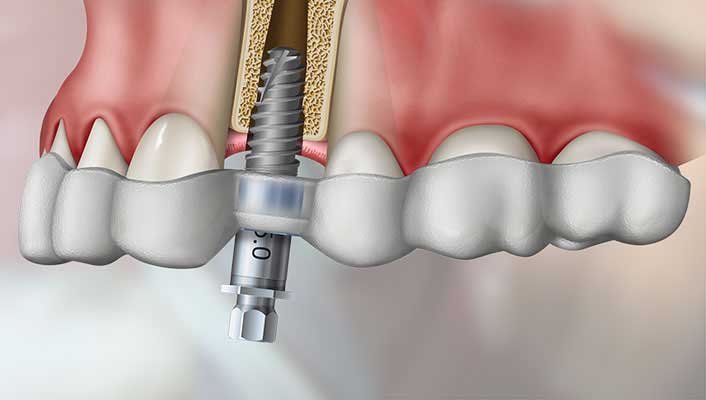
- Implant Placement: During the surgery, the surgical guide is placed over the patient’s teeth, ensuring accurate positioning of the implants. The dentist will prepare the site through the guide to create the implant bed and then place the implant into the jawbone.
- Post-Operative Care: After the implant placement, the patient will be given instructions on how to care for the implant as it heals. Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor the progress of the healing process and ensure the success of the implant.
Guided implant surgery is a complex and precise procedure that requires specialized training and equipment. It is essential to choose a dentist who is experienced in this technique to ensure the best possible outcome.